How To Play Music in Odd Times

Playing music in odd time signatures can be challenging–especially if you have no idea what they are or how they work. Luckily, this blog post looks at time signatures and what makes them odd.
You can recognize odd time signatures in songs when they are tough to count or dance to–it’s like they’re skipping a beat.
Odd time signatures enable artists to harness their imagination’s depths, creating unconventional and unique music. They can be tough to grasp at first. But once you get the hang of them, they’re a piece of cake.
So let’s take a closer look at odd time signatures, their components, and their impact on music.

What is a time signature?
Time signatures determine the song’s rhythm.
In sheet music, they appear as two numbers, one on top of the other. For instance, the simplest and most common time signature is 4/4.
We use them to measure or organize songs by dividing them into smaller sections. This helps musicians with timing and makes the song easier to remember.
Time signatures consist of two elements, a beat and a measure or ‘bar‘.
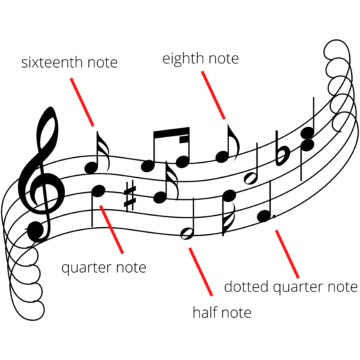
Beats & measures
In musical notation, the beat represents a basic unit of time. We organize beats in bars or measures. There are many types of beats, such as half beats, quarter beats, and eighth beats, to name a few.
The time signature’s top number is the number of beats in a bar, and the lower number refers to the type of beat that you’re playing. For instance, 5/8 is five eighth notes per measure. As you can see, songwriters have countless variations to play within musical notation.
So what’s the deal with an odd time signature?
Odd time signatures.
Also known as asymmetric, unusual, complex, or irregular time signatures, a song has an odd time signature when you can’t evenly divide the beats into the bar. For example, they appear in sheet music as 5/4, 11/4, 5/8, and even 23/16.
It’s always nice when things fit perfectly into their framework. However, in the case of music, a particular number of beats can produce intricate and pleasing sounds.
Odd time signatures are found in all types of music, including pop, electronic, and traditional, and they’re also popular in progressive rock and metal music.
Different types of odd time signatures.
When it comes to odd signatures, you can create almost anything you want. Although, some interesting examples could clarify the beat’s layout.
- 11/4—This signature contains eleven beats that are a quarter note each. We can break the beats down into 1-2-3, 1-2-3, 1-2-3, 1-2. You can also switch the beats to look like 1-2-3, 1-2, 1-2-3, 1-2-3, etc.
- 5/4—With five beats per measure, this time signature resonates at a frequency of a quarter note each. You can break this signature down into 1-2-3, 1-2, or 1-2, 1-2-3.
- 7/8—In this case, the signature has seven beats per measure, eight notes each 12-12-12- 1, or 123-12-12.
As you can see, you can use time signatures–especially odd ones–in interesting and unique ways.
How is odd time different from other signatures?
There are many different approaches that you can use regarding time signatures.
A signature is odd because the number of beats does not fit evenly into a measure. Their distribution must be in unique patterns, creating an unconventional rhythm.
Music has a host of other time signatures, and each offers a distinct rhythm. In a simple or normal time signature, you can divide beats into two equal sections of notes. The most common forms are 4/4, 2/4, and 3/4.
Compound signatures are similar to their simpler peers; only the beats break down into three equal parts. The introduction to Game of Thrones uses a 6/8 time signature. Some other common forms include 9/8, 12/8, and 3/8.
Another interesting way to write music–perhaps more peculiar than the odd time signature–is the changing, or polymetric time signatures. Using a changing time signature, you can play with beats and measures, establishing a new rhythm as the song progresses.
Popular songs with an odd time signature.
Part of understanding odd time signatures is identifying their sound. Here’s a list of songs that harness irregular beats to capture their listeners’ attention, love, and praise.
- The Ocean by the timeless rock band Led Zeppelin. The song’s musical time signature operates within a 7/8 framework.
- MGMT, a famous indie rock band, composed Electric Feel, which uses a 6/4 rhythm.
- Pink Floyd’s hit, Money, with a time signature of 7/4.
- You by Radiohead uses a changing time signature, mixing some simple and odd time signatures! The rhythm changes between 6/8 and 5/8.
Cool stuff right?
The more you practice listening to songs that use odd time signatures, the easier they are to identify, giving you a clearer idea of how they work.
However, like any skill, it takes time and practice.
Learn how to play the songs you love in various musical time signatures with JoyTunes. Our app Simply Piano guides you through a custom lesson plan that helps you progress one step at a time.
You’ll be playing your favorite songs in no time!